Authenticate with Gatekeeper
Bespot authentication is based on OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials Flow, as defined in RFC 6749, section 4.4, for authenticating clients and authorise them to access protected resources. This page is organised to depict this flow, describe the related components and, finally, provide instructions for a client on how to achieve that.
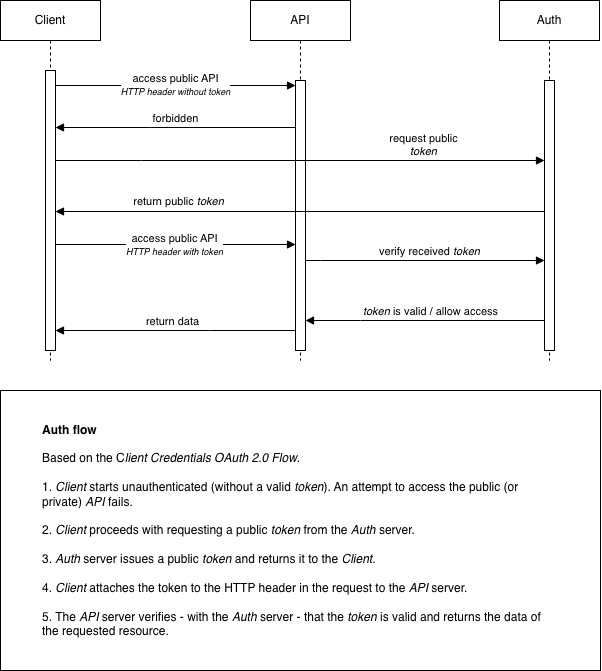
Components
Client
The client is either Bespot’s SDKs that request access to resources or any 3rd party server that needs to be authenticated and communicate securely with the system. The client needs to provide valid credentials, acquire an access token and, finally, use it for accessing protected resources.
Gatekeeper Auth
Bespot Gatekeeper uses an external Auth server for authenticating clients. To achieve that, OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials Flow is used. More specifically, a client id and a client secret need to be provided as input to the /oauth2/token endpoint. Then, if the credentials provided are valid, the authentication is successful and an access token is returned. The access token is in the form of JWT based on RFC 7519. Finally, this access token is used to retrieve resources from the Gatekeeper API (see below). The access token is only valid for a predefined period. If the access token expires, the client needs to start over with the authentication process and acquire a new one.
Gatekeeper API
Bespot’s Gatekeeper API is a collection of protected resources. To consume any Gatekeeper API resource, the Authorization HTTP header is required. Firstly, each client needs to be authenticated with the Gatekeeper Auth server providing the authentication credentials and acquire a valid access token.
Usage
See below the details of the authentication request to acquire the JWT access token.
Resource [POST]
[{AUTH_SERVER_URL}/oauth2/token]
The AUTH_SERVER_URL is provided securely along with the credentials.
Request
Headers
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedAuthorization: Basic Base64Encode(client_id:client_secret)
Example
The following is an authorization header for app client
djc98u3jiedmi283eu928with client secretabcdef01234567890, using the Base64-encoded version of the stringdjc98u3jiedmi283eu928:abcdef01234567890:Authorization: Basic ZGpjOTh1M2ppZWRtaTI4M2V1OTI4OmFiY2RlZjAxMjM0NTY3ODkw
Body
grant_type should also be set to client_credentials and passed as url encoded data.
Response
Body
The response is in JSON format and has the following structure:
{
"access_token": "{JWT-ACCESS-TOKEN}",
"expires_in": 86400,
"token_type": "Bearer"
}
Example cURL
curl --location '{AUTH_SERVER_URL}/oauth2/token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic ZGpjOTh1M2ppZWRtaTI4M2V1OTI4OmFiY2RlZjAxMjM0NTY3ODkw' \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials'
Authorization in Gatekeeper API
Bespot, along with access tokens, uses API keys to authorize different types of clients to access different types of resources.
-
The acquired access token should be provided in each Gatekeeper API request for the client to be authorised to access the resources. The
AuthorizationHTTP header should be filled with the acquired JWT access token prefixed with the following string:Bearer. -
The acquired API Key should be provided in each Gatekeeper API request to allow access to resources corresponding to specific client types.
Usage
Each client connected to Gatekeeper API should provide both the acquired API Key and the acquired access token as HTTP headers in each request.
Example
x-api-key: {X-API-KEY}
Authorization: Bearer {JWT-ACCESS-TOKEN}
The X-API-KEY is provided securely along with the credentials.